Controlling spin for memory storage
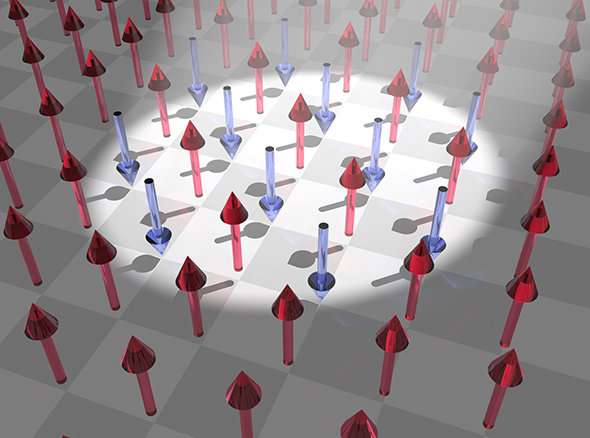
Tohoku University researchers have developed a computational simulation that shows that using ultrafast laser pulses to excite electrons in a magnetic material switches them into a transient non-magnetic state. This could reduce the time involved in manipulating a material's magnetism, improving magnetic storage and information processing technologies.
Storing bits, or binary digits, of information in magnetic memory devices requires the ability to reverse the magnetism within a material between ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic. In the ferromagnetic state, the electron spins within the material align parallel to each other and spin in the same direction, making them and the material magnetic. In the antiferromagnetic state, the electron spins align parallel to each other but neighbouring electrons spin in opposite directions, cancelling out each other's effects and making them and the material in which they exist virtually non-magnetic.
Fast memory storage requires rapid spin reversal. Researchers have been studying ways to control it using ultrafast lasers to get even faster memory storage. The shorter the laser's pulse, the faster the reversal will be.
Tohoku University physicists Atsushi Ono and Sumio Ishihara developed a computational approach to model how electrons and their spins interact with each other and react to laser light.
They found that exposing electrons in ferromagnetic materials to a continuous laser light makes them excited, causing electron interactions that lead to an antiferromagnetic state. Applying ultrafast light pulses also leads to switching from ferromagnetism to transient antiferromagnetism, followed by recovery of ferromagnetism. When the researchers applied an ultrafast laser pulse followed by a continuous laser light, the electrons were manipulated into an antiferromagnetic state that was then maintained by the continuous light. Removing the continuous light caused the gradual disappearance of the antiferromagnetic state.
Understanding these interactions, as well as the fundamental limits of spin reversal, is necessary for future development of magnetic memory devices. The next step will require physical experiments to test the model's predictions.
"Experimental confirmations are indispensable for establishing the present proposal," the researchers write in their study, which was published in the journal Physical Review Letters. Ono and Ishihara suggest perovskite manganites and layered manganites as possible materials for testing their model. They also suggest a variety of techniques, such as magnetic x-ray diffraction and photoemission spectroscopy, for observing the transient antiferromagnetic state.
More information: Atsushi Ono et al, Double-Exchange Interaction in Optically Induced Nonequilibrium State: A Conversion from Ferromagnetic to Antiferromagnetic Structure, Physical Review Letters (2017). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.207202
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Tohoku University